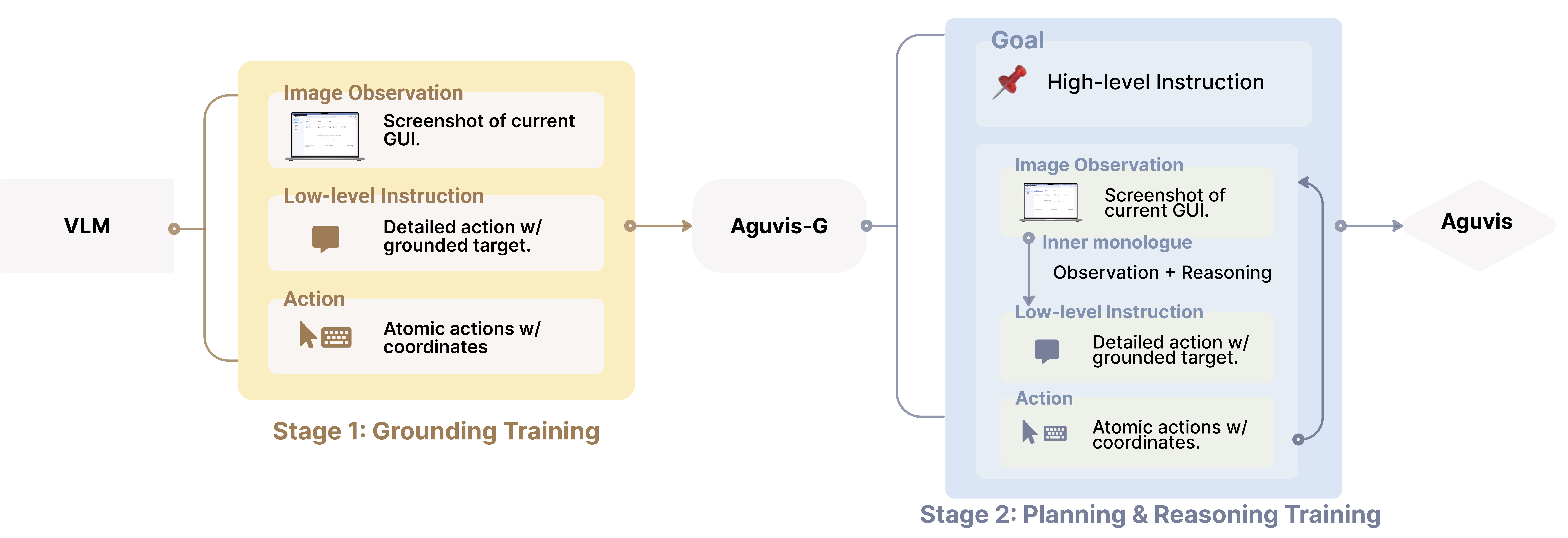
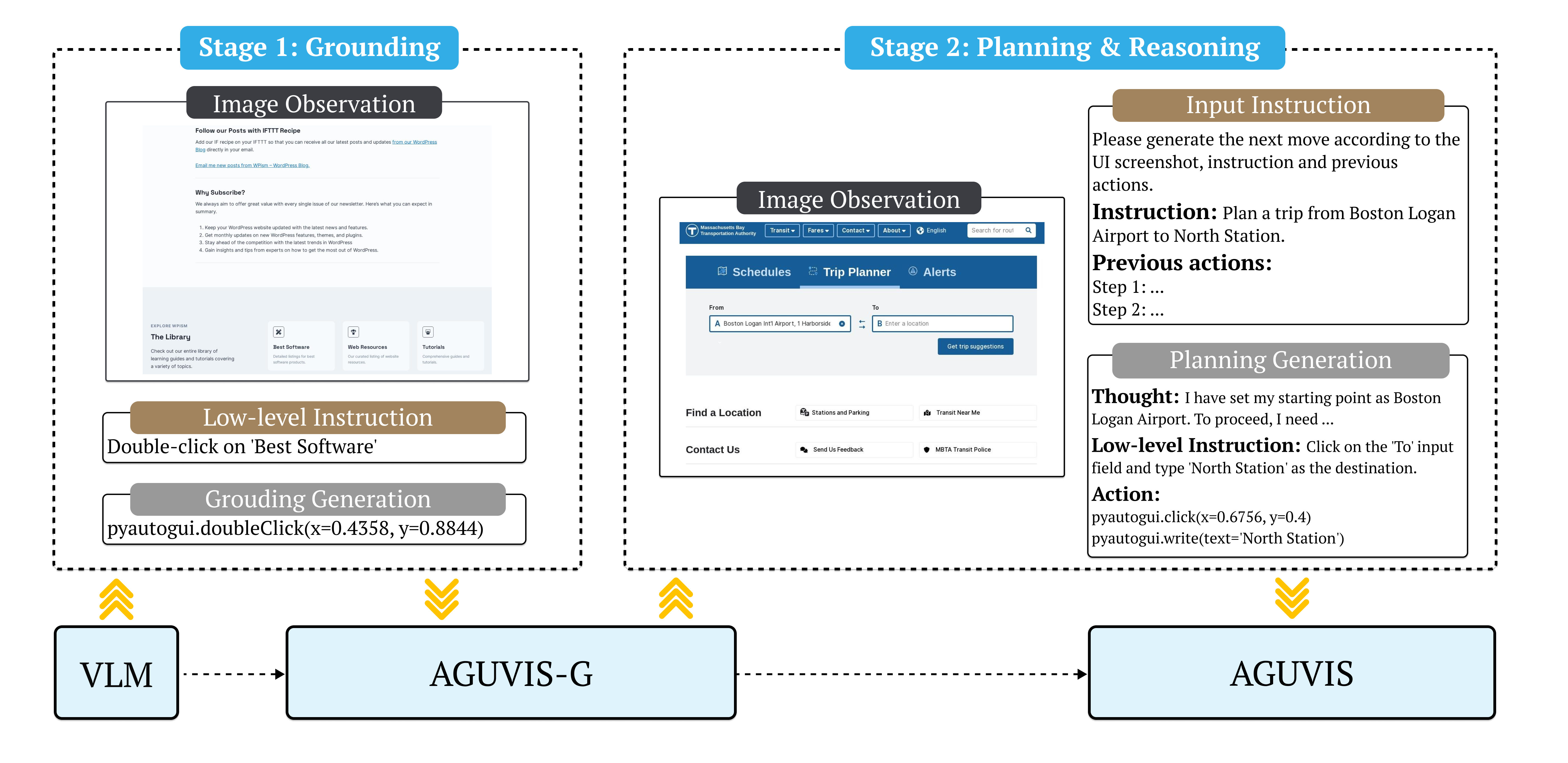
AGUVIS is a unified pure vision-based framework for autonomous GUI agents that can operate across various platforms (web, desktop, mobile). Unlike previous approaches that rely on textual representations, AGUVIS leverages unified purely vision-based observations and a consistent action space to ensure better generalization across different platforms.
Our framework demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in both offline and real-world online scenarios, offering a more efficient and generalizable approach to GUI automation.
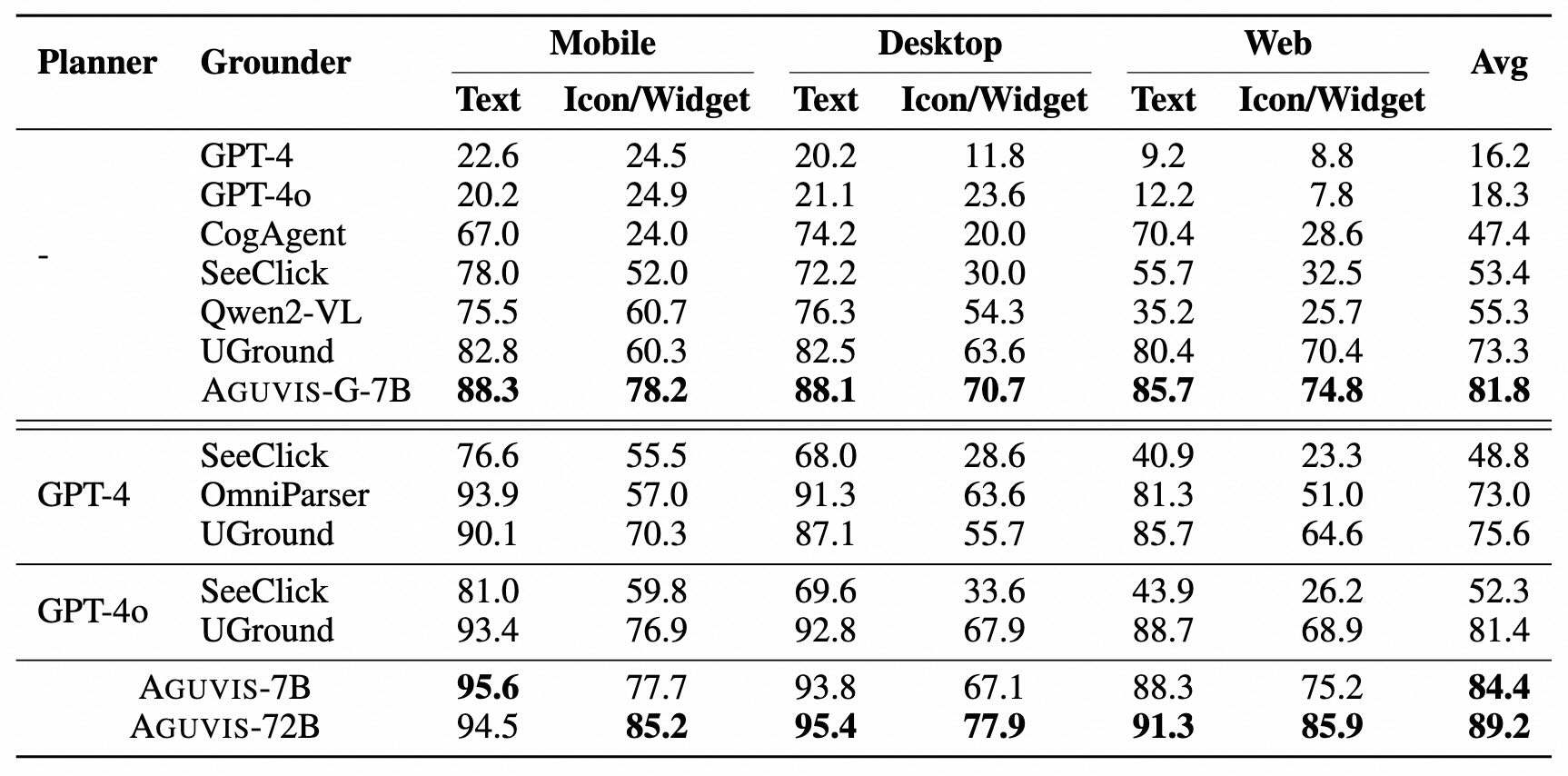
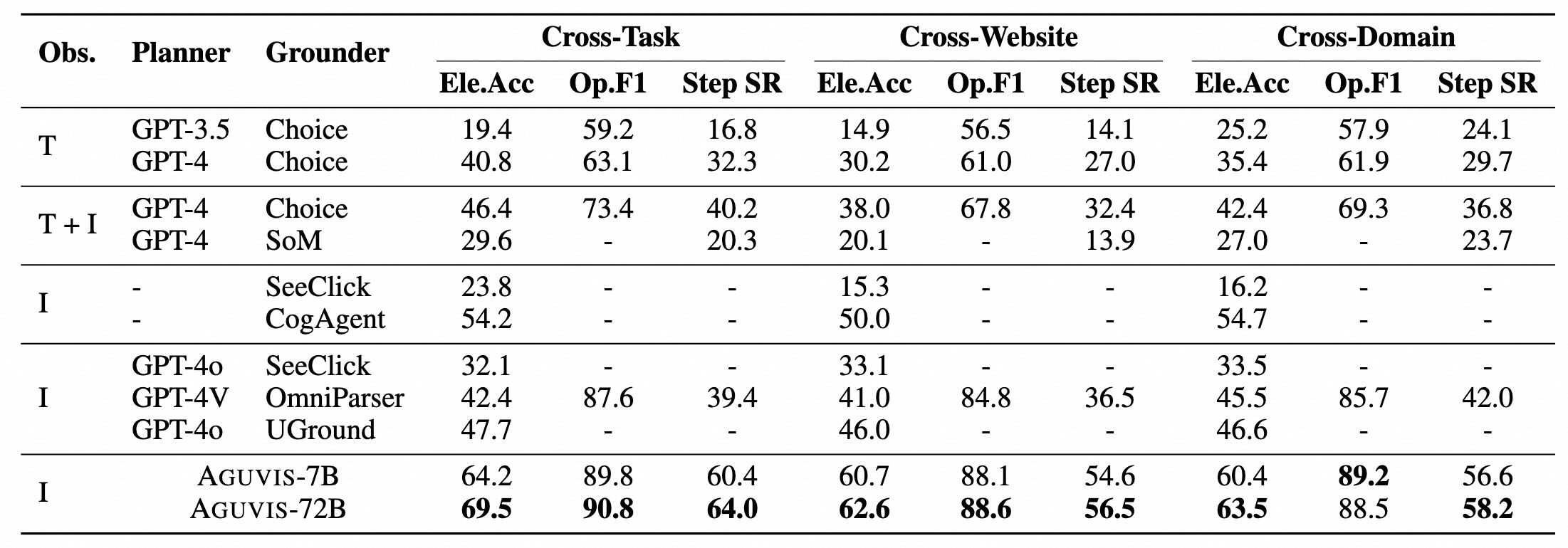
| Planner | Grounder | OS | Calc | Impress | Writer | VLC | TB | Chrome | VSC | GIMP | WF | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o | 8.33 | 0.00 | 6.77 | 4.35 | 16.10 | 0.00 | 4.35 | 4.35 | 3.85 | 5.58 | 5.03 | |
| GPT-4o | SoM | 20.83 | 0.00 | 6.77 | 4.35 | 6.53 | 0.00 | 4.35 | 4.35 | 0.00 | 3.60 | 4.59 |
| SecClick | 16.67 | 0.00 | 12.76 | 4.35 | 23.52 | 6.67 | 10.86 | 8.70 | 11.54 | 7.92 | 9.21 | |
| OS-Atlas-Base-4B | 20.83 | 2.23 | 14.89 | 8.70 | 23.52 | 13.33 | 15.22 | 13.04 | 15.38 | 7.92 | 11.65 | |
| OS-Atlas-Base-7B | 25.00 | 4.26 | 17.02 | 8.70 | 29.41 | 26.67 | 19.57 | 17.39 | 19.23 | 8.91 | 14.63 | |
| AGUVIS-7B | 41.67 | 4.26 | 8.51 | 17.38 | 17.65 | 26.67 | 17.23 | 17.39 | 34.62 | 5.58 | 14.79 | |
| AGUVIS-72B | 20.83 | 4.26 | 11.03 | 13.04 | 12.41 | 20.00 | 15.06 | 17.39 | 11.54 | 3.60 | 10.26 | |
| Human | 75.00 | 61.70 | 80.85 | 73.91 | 70.59 | 46.67 | 78.26 | 73.91 | 73.08 | 73.27 | 72.36 | |
@misc{xu2024aguvis,
title={Aguvis: Unified Pure Vision Agents for Autonomous GUI Interaction},
author={Yiheng Xu and Zekun Wang and Junli Wang and Dunjie Lu and Tianbao Xie and Amrita Saha and Doyen Sahoo and Tao Yu and Caiming Xiong},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.04454},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}